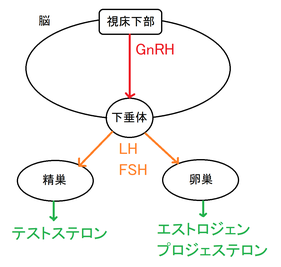
エストロジェンやアンドロジェンの投与による避妊は、「性ホルモンが十分に存在するから、性腺刺激ホルモンの分泌を止めてもいい」と視床下部や下垂体に働きかける「負のフィードバック」を利用していました。次世代のホルモン避妊薬は、視床下部から下垂体に性腺刺激ホルモンの分泌を指示するGnRHの働きを止めることに主眼が置かれました。下垂体がGnRH類似物質に常にさらされることにより、下垂体のGnRHに対する感受性を低下させる「ダウンレギュレーション」を利用しようとしたわけです。Alliance for Contraception in Cats & Dogs (猫と犬の避妊のための同盟:ACC&D)のレポート"Contraception and Fertility Control in Dogs and Cats"(2013)にはこう記述されています。
The next hormonal approach to contraception in small animals to be developed was gonadotropin- releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs. The advantage to using GnRH or its analogs is that these compounds are effective in males and females, since GnRH is the master control hormone for reproduction. Also, the GnRH decapeptide has the same amino-acid sequence in all mammals, making any product potentially useful in a variety of species. The development of long-acting preparation of the GnRH agonists has long been sought. Compounds began to emerge as promising candidates. Long-acting powerful analogs have been shown to occupy GnRH receptors at the pituitary and after a short period of stimulation cause the cells to reduce or stop the synthesis of the receptor protein, making the cells insensitive to GnRH. This process is called receptor down-regulation. As down-regulation occurs, production of gonadotrophins by the pituitary (luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)) ceases, effectively shutting down spermatogenesis and androgen production in the male and cyclic ovarian function in the female.
小動物におけるホルモンによる避妊法として、次に開発されたのがゴナドトロピン放出ホルモン(GnRH)類似体でした。GnRHまたはその類似体を使用する利点は、GnRHが生殖を主に制御するホルモンであるため、これらの化合物がオスとメスに有効であることです。また、GnRHのデカペプチドはすべての哺乳類で同じアミノ酸配列を持つため、どの製品も様々な動物種に有用である可能性があります。このGnRH作動薬の長時間作用型製剤の開発は、古くから求められていました。そして有望な候補となる化合物が出現し始めました。長時間作用型の強力な類似体は、下垂体のGnRH受容体を占拠し、短時間の刺激で細胞に受容体タンパク質の合成を減少または停止させ、細胞をGnRHに対して非感受性にすることが示されてきました。この過程を受容体ダウンレギュレーションと呼びます。ダウンレギュレーションが起こると、下垂体からの性腺刺激ホルモン(黄体形成ホルモン(LH)と卵胞刺激ホルモン(FSH))の分泌が止まり、オスでは精子形成とアンドロジェン産生、メスでは周期的卵巣機能を効果的に停止させることができるようになります。(p14)